Joint type
Stability factors of the joint – names of the ligaments which provide support (eg coracoacromial) and their positions in relation to the joint.
The components of the coraco-acromial arch.
The muscles and tendons which provide stability (eg rotator cuff).
Curriculum
The shoulder joint is an articulation between – Head of the Humerus & Glenoid cavity of Scapula
It’s a Synovial Ball and Socket type of joint.
Ligaments of shoulder joint
Each ligament is named based on the parts they connect. Just read the ligament name carefully and you’ll understand it’s location logically.
Glenohumeral
It connects Glenoid labrum and Humerus in front of the joint. Shown in the image in purple.
Coracohumeral
Coracoid process of Scapula to greater tubercle of Humerus, On superior aspect of the joint, shown in Red in the image.
Coracoacromial / accessory ligament
Between the Acromion process and coracoid process of Scapula. Forms the Coraco-acromial arch. It prevents superior displacement of the humeral head.
Less important
Coracoclavicular has trapezoid and conoid ligaments – from Clavicle to Coracoid process of the scapula.
Transverse humeral – between the two tubercles.
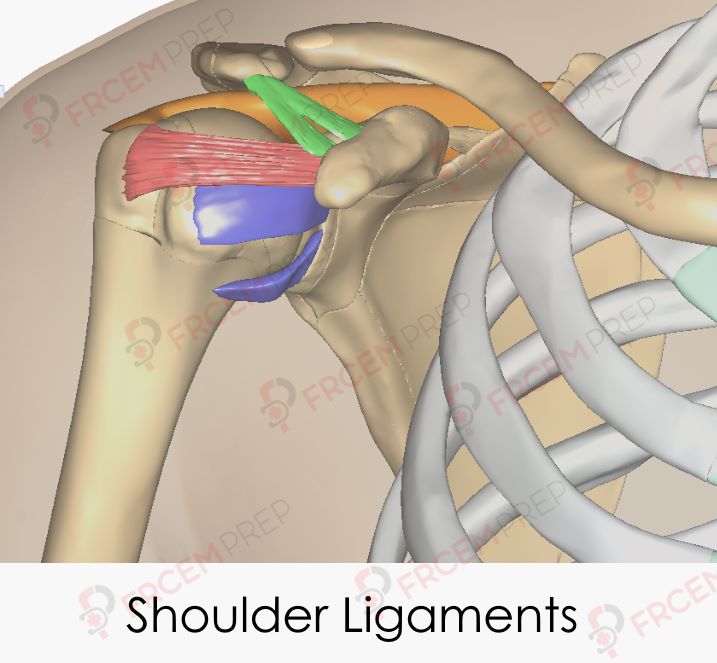
Shoulder ligaments – Image modified from BodyParts3D, © The Database Center for Life Science licensed under CC Attribution-Share Alike 2.1 Japan
Glenohumeral – Purple
Coracohumeral – Red
Coraco-acromial – Green
Supraspinatus muscle – Orange (Impacted in impingement syndrome)
Impingement syndrome
The space underneath the Coraco-Acromial ligament is less and Suprascapular muscle passes through this narrow space. If the ligaments is thickened, the space becomes much narrower and the muscle gets pressed/impinged in full abduction of Shoulder joint. Impingement Syndrome.
Rotator Cuff
The Rotator Cuff includes a group of 4 muscles that arise from Scapula and their tendons insert on the head of Humerus to provide strength and stability to the shoulder joint. They form a cuff around the Gleno-Humeral joint, hence named the Rotator cuff.
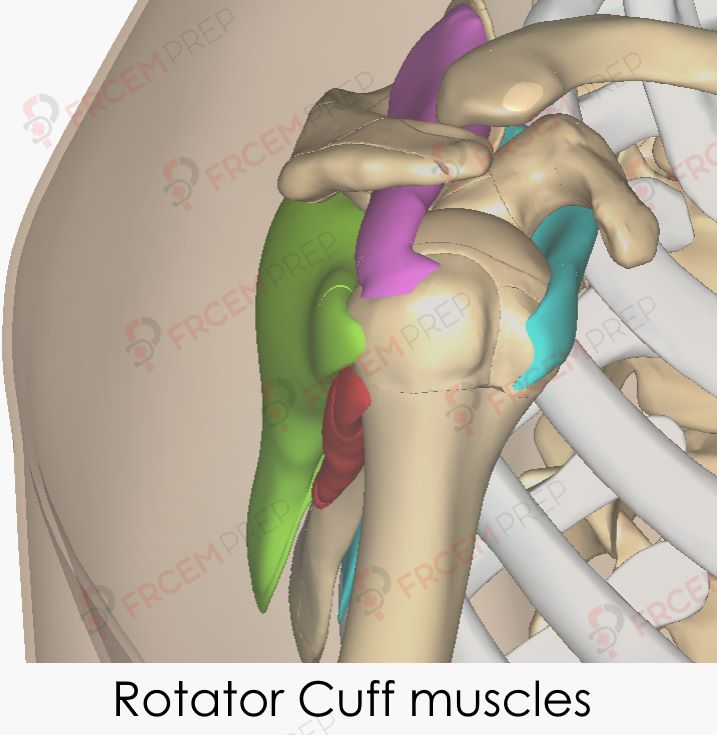
Rotator cuff muscles – Image modified from BodyParts3D, © The Database Center for Life Science licensed under CC Attribution-Share Alike 2.1 Japan
The 4 muscles of Rotator cuff shown in image:
- Supraspinatus – Pink
- Infraspinatus – Green
- Teres minor – Red
- Subscapularis – Cyan